
If a file or object is accessed locally, the NTFS permissions will be applied, but if an object is shared, then both sets of permissions activate, and the most restrictive permission is applied. NTFS permissions and share permissions can be applied in tandem. There’s also an advanced NTFS permissions list, which provides admins with more granular control over permissions access levels, though the specific permissions will vary based on object type. Typically, this is done by using NTFS to modify permissions to a root folder, which subfolders and files then inherit by default (though this feature can be disabled as needed).īasic NTFS permissions allow administrators to control end-user access levels for multiple functions, including: NTFS file systems operate by applying permissions to files, folders, drives, containers, and other objects.
NTFS PERMISSIONS WINDOWS
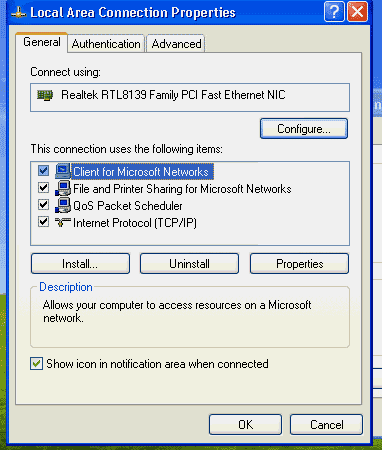
NTFS folder permissions and other shared resource permissions can be applied to both local and networked users, so when someone logs into any Windows workstation on the network, or via a remote connection, they’ll receive the same set of NTFS file permissions. In addition to Windows folder permissions, NTFS permissions utilities can also be used to grant or restrict access to network containers and Active Directory objects. NTFS share permissions can be applied to any NTFS-formatted drive. NTFS is the file system formatting used by all Windows operating systems and gives admins control over inherited permissions passed down to individual files and folders. By configuring the user account, group member, and domain access permissions applied to network drives, files, and folders, administrators enable individual end users to share and exchange resources and can improve security by restricting access to sensitive or confidential materials. New Technology File System or NTFS permissions control the specific shared resources end-user accounts have access to.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
